Perform β-Ketone and Glucose testing anywhere
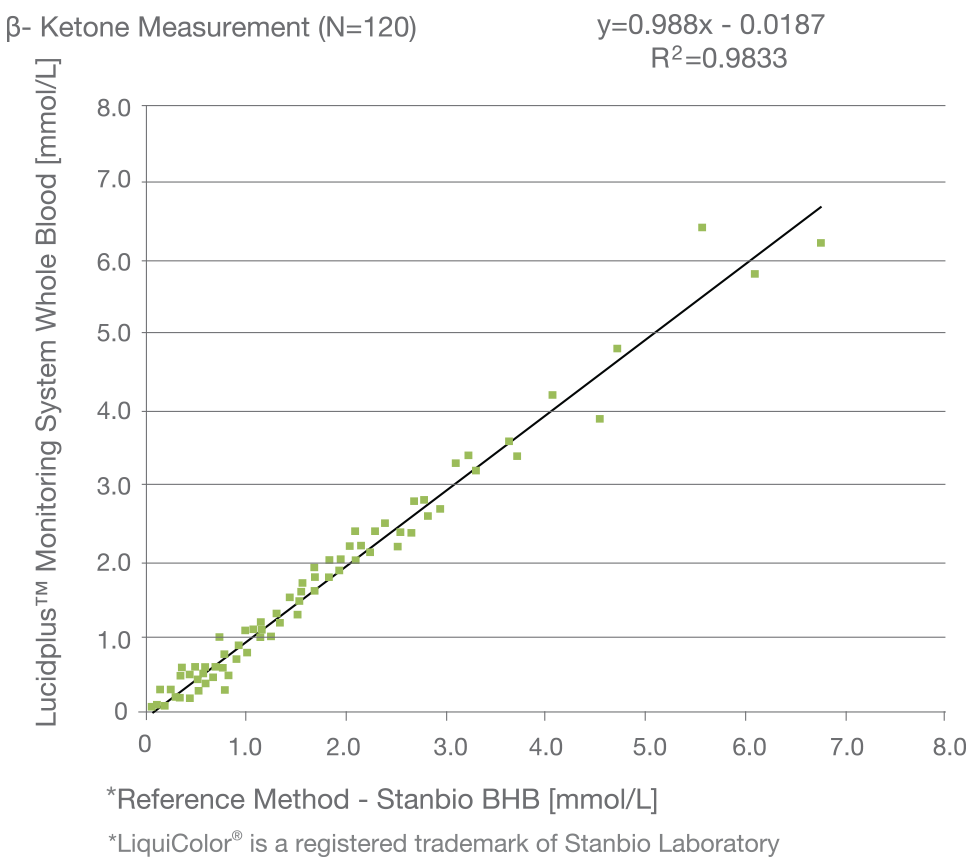
Lucidplus™ allows you to monitor DKA patients with the convenience of using this device anywhere in your facility.
1Utilizing point-of-care β-OHB testing has the potential to reduce comprehensive laboratory evaluations for DKA among hyperglycemic emergency-department patients.
2DKA was defined according to the American Diabetes Association (ADA) criteria:
- Serum glucose_>250 mg/dL
- Anion gap >10 mmol/L
- Carbon dioxide _< 18 mmol/L and ph _<7.3
1 ,2 Arora, Sanjay, MD, Henderson, Sean O, MD, Long, Theodore, Long, MD, Menchine, Michael, MD, MPH, “Diagnostic Accuracy of Point-of-Care Testing for Diabetic Ketoacidosis at Emergency-Department Triage, β-Hdroxybutyrate versus the urine dipstick.” Diabetes Care 34 (2011) 852-852. 3 Feb 2018 Accessed.
Training Video
Diabetic ketoacidosis
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a complication of diabetes that occurs when ketones build up in the bloodstream. When your cells don’t get the glucose they need for energy, your body begins to burn fat for energy, which produces ketones. High levels of ketones can poison the body and cause DKA. DKA can lead to diabetic coma or even death. Early diagnosis, monitoring and treatment are usually very effective at preventing serious complications.
Correlates to β-Hydroxybutyrate LiquiColor® Reagent*